IPB University Students Create Natural 3-in-1 Hydrogel for Burn Treatment

Burns remain a serious global health problem. According to data from the World Health Organization (WHO), more than 11 million people suffer burns every year, 90 percent of which occur in low and middle income countries.
Second-degree burns are the most common type, accounting for 85 percent of all cases, and carry a high risk of infection that can progress to sepsis if not properly treated.
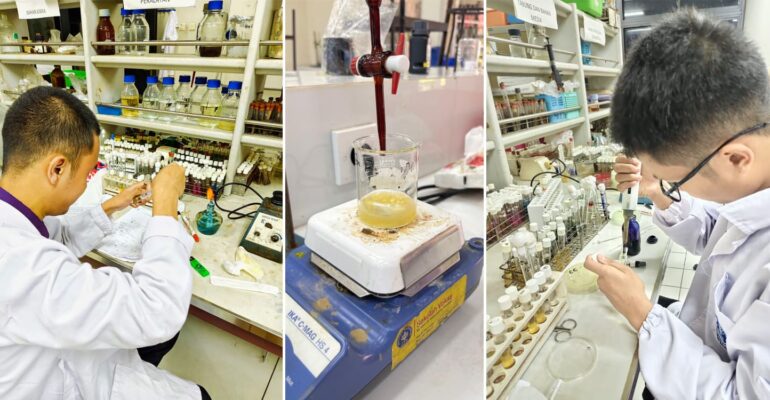
In response to this challenge, a team of students from IPB University who are members of the Exact Research Student Creativity Program (PKM-RE) presented an innovation in the form of a 3-in-1 burn hydrogel with antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, and skin tissue regeneration properties.
The research team consists of Darma Aji Nugraha, Muhammad Anwar Taufik, Say Qanaah Garda Mudi II, Jason Raditya Santosa, and Revia Syafutri. This research was supervised by Dr Diah Nugrahani Pristihadi, a lecturer at the IPB University School of Medicine and Biomedicine.
Team leader Darma Aji Nugraha explained that this product is formulated from natural ingredients sourced locally in Indonesia, namely kepok banana peel (Musa paradisiaca), butterfly pea flower (Clitoria ternatea L.), and aloe vera.
“Each ingredient has an important role. Banana peel contains flavonoids and trigonelline, which act as anti-inflammatories to reduce inflammation. Butterfly pea flowers are rich in flavonoids, anthocyanins, and saponins, which have antibacterial properties and prevent the formation of biofilms that cause infections,” he said.
Meanwhile, aloe vera combined with silver nanoparticles has been proven to stimulate collagen formation and accelerate the regeneration of damaged skin.
“By combining these three ingredients, we hope that this hydrogel will not only prevent infection but also accelerate the recovery of burns so that patients can recover more optimally,” said Darma.
Initial results show that a one percent concentration of butterfly pea flower extract is effective in inhibiting the growth of Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli, two major pathogenic bacteria in burns, with effectiveness comparable to the antibiotic gentamicin.
The developed hydrogel formulation has also been tested in vivo and shows significant acceleration in wound healing.
“Although research is ongoing, the preliminary results open up great opportunities for further development. The team is currently conducting tissue regeneration analysis through histology and immunohistochemistry (IHC) tests to strengthen the scientific data,” said Darma.
In line with this, Dr Diah, as the supervising lecturer, hopes that this research can become an effective, affordable, and environmentally friendly herbal therapy alternative, providing tangible benefits for the community. (**/dr) (IAAS/FMT)