Wildlife Ecology Expert at IPB University: The Fragrance of Pandan Luwak Civets is a Sign of Forest Life
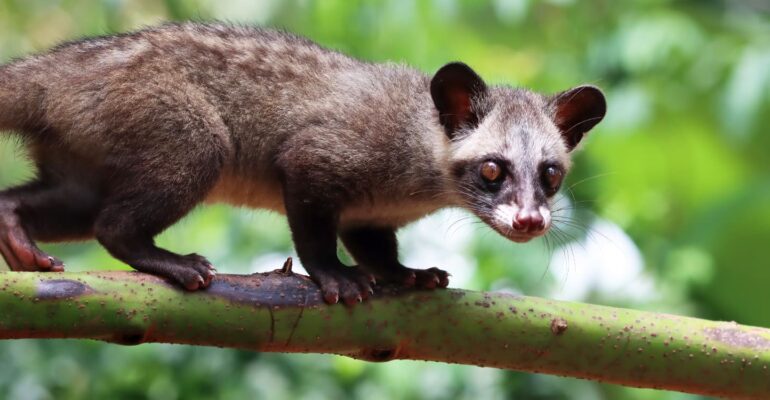

Luwak civets (Paradoxurus hermaphroditus) is not only known for its role in producing luwak coffee. This mammal also has unique glands that can emit a pandan-like aroma.
“This scent plays an important role in social interactions and self-defense,” said Dr Abdul Haris Mustari, Wildlife Ecology Expert and lecturer in Forest Resource Conservation and Ecotourism at IPB University.
The pandan-scented glands are located at the base of the tail near the anus and on the underside of the civets abdomen. “These glands produce a mixture of proteins, fats, and volatile chemical compounds. This distinctive scent is known as the pandan gland,” he explained.
Furthermore, Dr Haris elaborated on the functions of the pandan gland, which include marking territory, social and reproductive communication, and as a self-defense mechanism. “This scent helps civets recognize each other, attract mates, avoid conflict, and even signal warnings to predators,” he added.
Naturally, civets are found in Sumatra, Java, Kalimantan, and have been introduced to eastern Indonesia, such as Sulawesi, Maluku, and Nusa Tenggara. Their existence in the wild is now increasingly threatened due to habitat loss, hunting, and trade.
“Unfortunately, the civet population continues to decline. Civets are often considered pests because they prey on poultry, even though their natural diet consists of fruits, reptiles, and rodents. In fact, civets play an important role in natural pest control,” said Dr Haris.
In addition to maintaining pest population balance, luwak civets also play a role in spreading plant seeds. When they eat fruit, the seeds are carried out with their feces and grow into new plants. This process supports forest regeneration.
“Civets even help break the dormancy of seeds from palm fruits, such as enau and forest areca, as well as many other types of plants, so that they can germinate better,” he added.
On the other hand, civets also have economic value. On coffee plantations, civets are deliberately raised to produce the famous high-quality and expensive civet coffee. In fact, the natural pandan aroma of civets is used as a base ingredient in perfumes in several fragrance-producing countries.
Dr Haris emphasized that if the civet population continues to decline, there will be a chain reaction on the ecosystem. Pest outbreaks could increase, forest regeneration could be disrupted, and the ecological function of civets could be lost.
“Civets are part of our biological wealth that must be preserved. Let them live and reproduce naturally so that the ecosystem remains balanced,” he said. (dr) (IAAS/LAN)