The Secret of Herbs Behind Sijaka, Prof Mega Safithri’s Innovation to Overcome Diabetes

Professor of Nutritional Biochemistry at IPB University, Prof Mega Safithri, said that the potential of herbal medicine in Indonesia is very promising. According to her, public awareness of the need for natural treatments with minimal side effects is now increasing.
“With scientific studies on toxicity, safety, and efficacy, the development of herbal medicine can be more trusted,” said Prof Mega in her Scientific Lecture as a Professor at IPB University on (8/30).
In her research, Prof Mega and her team discovered active compounds in several herbal plants, such as piperine and piperanine in red betel leaf, gingerol in red ginger, and cinnamaldehyde and cinnamic acid in cinnamon.
“These compounds have been proven to play a role in lowering blood glucose levels and reducing inflammation in diabetes patients,” she explained.
Prof Mega explained that herbal medicine research, particularly for diabetes mellitus (DM), can be conducted through a medical biochemistry and nutrition approach. One of the mechanisms is testing the bioactivity of herbs against blood sugar-regulating enzymes, such as amylase and alpha-glucosidase, through computational simulation.
“If the potential is significant, the research continues with in vitro and in vivo tests on animals before proceeding to the clinical trial stage on humans,” she explained.
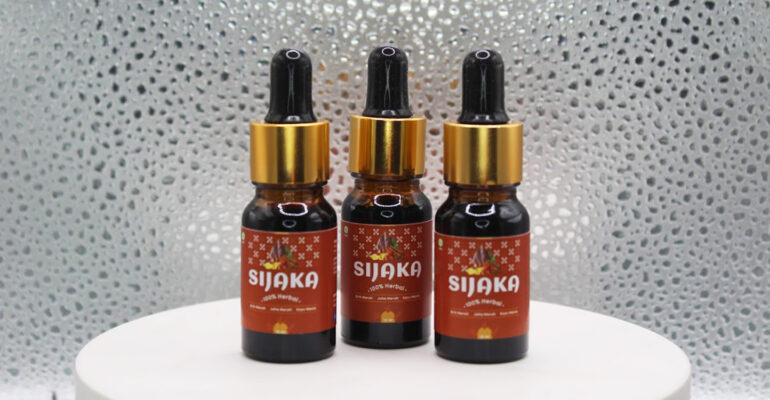
One of the herbal products resulting from Prof Mega and her team’s research is Sijaka. This product has been commercialized since 2022. Several user testimonials mention significant improvements, such as reduced tremors, improved HbA1c levels, and readiness for eye surgery.
However, Prof Mega explained that Sijaka’s distribution permit is still awaiting the completion of requirements by its industry partner, PT Nano Herbaltama, which is targeted for completion in August 2025.
Prof Mega also emphasized the need for public education and the role of doctors in supporting evidence-based herbal use. “IPB University now has a Faculty of Medicine and is collaborating with several hospitals, including Cibinong Regional General Hospital and Airlangga University Teaching Hospital, for the development of herbal supplements for diabetes therapy,” she stated.
Looking at global trends, Prof Mega is optimistic that Indonesia has a significant opportunity to become a global hub for herbal medicine research and investment within the next 10 years. With government support and collaboration with the IPB University Center for Tropical Biopharmaceutical Studies, it is hoped that thousands of herbal medicine patents based on scientific research can be achieved.
“The hope is that, through evidence-based research, Indonesia can become a major player in the global herbal medicine industry,” she said. (dr) (IAAS/STD)