Prevent Serious Effects of Neuropathy, IPB University Faculty of Medicine Lecturer Calls for Early Detection
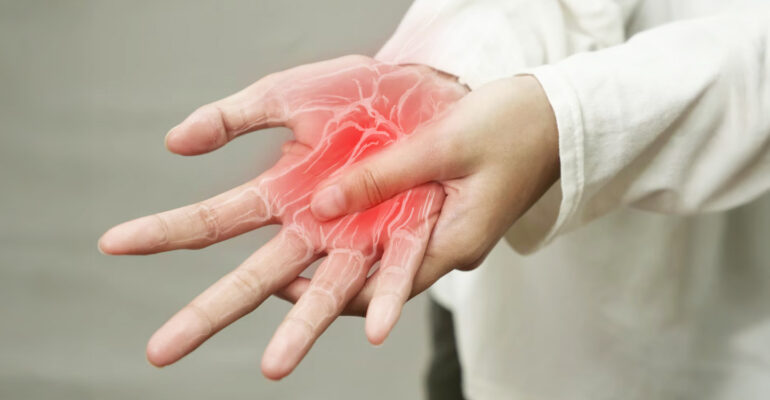
Neuropathy, or damage to the peripheral nerves, can have serious effects if not detected early. This disorder can cause decreased bodily function, chronic wounds, and even amputation. Therefore, it is important for the public to understand the symptoms early on.
This was emphasized by dr Yeni Quinta Mondiani, SpN, a neurology expert and lecturer at the Faculty of Medicine, IPB University. “Neuropathy is defined as damage to nerves,” explained dr Yeni during the IPB Podcast on the IPB TV YouTube channel recently.
She elaborated that peripheral nerves consist of sensory nerves (responsible for sensation), motor nerves (responsible for movement), and autonomic nerves (regulating automatic body functions such as heartbeat). Symptoms of neuropathy vary depending on the type of nerve affected, although they typically begin with sensory nerve dysfunction.
“For sensory nerves, it is further divided into two categories: positive symptoms and negative symptoms,” she explained. Positive symptoms include sensations that should not be present, such as a feeling of being crawled on by ants, sharp stabbing pains, or burning pain. Negative symptoms are characterized by the loss of sensation, such as numbness or tingling.
If the motor nerves are affected, symptoms include muscle weakness, such as difficulty gripping or opening bottles.
dr Yeni said that neuropathy is not a single disease, but a syndrome with various causes. “The main cause of peripheral neuropathy is diabetes mellitus. The progression from diabetes to neuropathy is estimated to take around 3–5 years,” she explained.
Other causes include genetic factors (though rare), side effects of medications (such as antibiotics, heart medications, or chemotherapy), vitamin deficiencies (especially B1, B6, B12, and E), exposure to toxic substances (heavy metals, pesticides), and nerve injuries or compression, such as in Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) caused by repetitive movements or prolonged typing. Autoimmune diseases can also cause neuropathy, as the immune system attacks nerve cells.
dr Yeni emphasized that neuropathy does not only affect the elderly. “There are many cases of diabetes nowadays. Even young people aged 20 can develop neuropathy,” she said. She added that students and office workers who stare at screens or type for long periods of time without a break are also at risk of neuropathy due to pressure on the nerves.
According to her, people need to see a doctor immediately if they experience sudden numbness or tingling, especially if they have no risk factors. “If there are no risk factors and you suddenly experience numbness or tingling, you should be careful. It could be a symptom of a stroke or Guillain-Barré Syndrome,” she said. For those with risk factors, a check-up is recommended if symptoms do not improve within 2–3 weeks despite taking nerve vitamins.
She also emphasized the importance of prevention through a healthy lifestyle. “Nutrition is the first priority. Long-term alcohol use and smoking are also risk factors,” she explained. She advised against engaging in monotonous activities, such as typing, for more than 30–60 minutes without a break. “Normally, we need to stretch our eyes, wrists, and waist,” she added.
Complications from untreated neuropathy can lead to a decline in quality of life, painless wounds, especially in people with diabetes, and severe infections that may result in amputation. This condition can also trigger psychological disorders such as depression.
“Prevent neuropathy early, take care of your nerves, take care of your health,” concluded dr Yeni. (Fj) (IAAS/LAN)